PHYTOR WELLNESS BLOOD SUGAR ACTIVE INGREDIENTS
Each of our chosen Herbs Contain in Excess of 3,000 Plant Compounds
From these we have isolated specific active ingredients which deliver targeted health benefits. We have shared our herbal formulations with over 10,000 patients who seek to use natural remedies to support their body’s natural healing abilities.
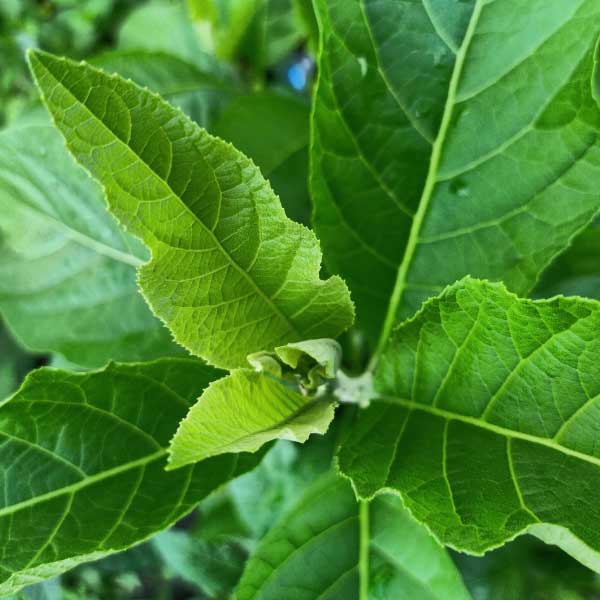
VERNONIA AMYGDALINA
Traditionally used in Ethiopia and tropical Africa as medicine for gastrointestinal disorders, and as a general tonic. The leaves are bitter and often used in combination with other herbs for kidney problems and to help maintain healthy blood sugar and blood pressure levels.
Contains saponins, alkaloids, terpenes, coumarins, flavonoids, phenolic acids, lignans, xanthones, anthraquinones, edotides and sesquiterpenes.
Native: Tropical Africa
Habitat: Wet forests and plains, mainly cultivated.
Plant Description: Large shrub with rough flaked barks and elliptic green leaves.
Please refer to the published research
Please refer to the published research
- Nguyen, T. X. T., Dang, D. L., Ngo, V. Q., Trinh, T. C., Trinh, Q. N., Do, T. D., & Thanh, T. T. T. (2021). Anti-inflammatory activity of a new compound from Vernonia amygdalina. Natural Product Research, 35(23), 5160-5165. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2020.1788556
- Mbatchou, V. C., Nabayire, K. O., & Akuoko, Y. J. C. S. (2017). Vernonia amygdalina Leaf: Unveiling its antacid and carminative properties In Vitro. Current Science, 3(3), 148-155.
- Kadiri, O., & Olawoye, B. (2016). Vernonia amygdalina: An underutilized vegetable with nutraceutical Potentials–A Review. Turkish Journal of Agriculture-Food Science and Technology, 4(9), 763-768. DOI: https://doi.org/10.24925/turjaf.v4i9.763-768.570
- Ifeoma, I. I., & Chukwunonso, E. E. (2011). Current perspectives on the medicinal potentials of Vernonia amygdalina Del. Journal of medicinal plants research, 5(7), 1051-1061. DOI: https://doi.org/10.24925/turjaf.v4i9.763-768.570
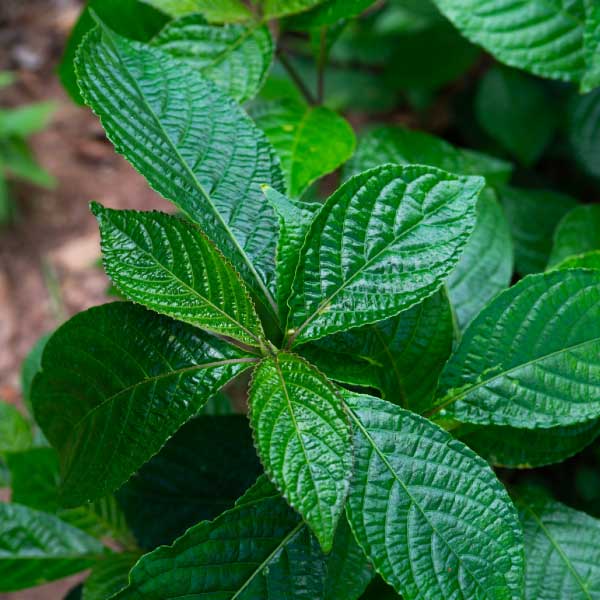
Strobilanthes crispus
Traditionally used in Indonesia and Malaysia to treat urinary stones, gallbladder stones, difficult urination, hemorrhoid, constipation, or for diuretic purpose.
Contains p-hydroxybenzoic acid, p-coumaric acid, caffeic acid, vanillic acid, gentinic acid, ferulic acid, syryngic acid, tannin alkaloid, catechin, rutin, myricetin, luteolin, apigenin, naringenin and kaempferol.
Native: Madagascar, Indonesia, Malaysia
Habitat: Wet forests and plains, mainly cultivated.
Plant Description: Shrub with dark green shiny leaves occurring in pairs in opposite leaf arrangement.
Please refer to the published research
Please refer to the published research
- Gul, M. T., Dheyab, A. S., Shaker, E. K., Muhammad, N., & Pauzi, A. N. (2020). In vitro evaluation of anti-urolithiatic properties of Strobilanthes crispus extracted using different solvents. Research Journal of Chemistry and Environment Vol, 24, 1.
- Ban, W. K., Fong, I. L., Khong, H. Y., & Phung, J. H. Y. (2022). Wound Healing, Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Properties of Clinacanthus nutans (Burm. f.) Lindau and Strobilanthes crispus (L.) Blume Extracts. Molecules, 27(5), 1722. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27051722
- Tobing, J. H. (2022). The Effect of Sambiloto (Andrographis paniculata Nees.) and Kejibeling (Strobilanthes crispa) Leaves on Uric Acid Levels of White Rats (Rattus norvegicus). 8ISC Proceedings: Sciences, 5-12. http://ejournal.unklab.ac.id/index.php/8ISCSC/article/view/668



